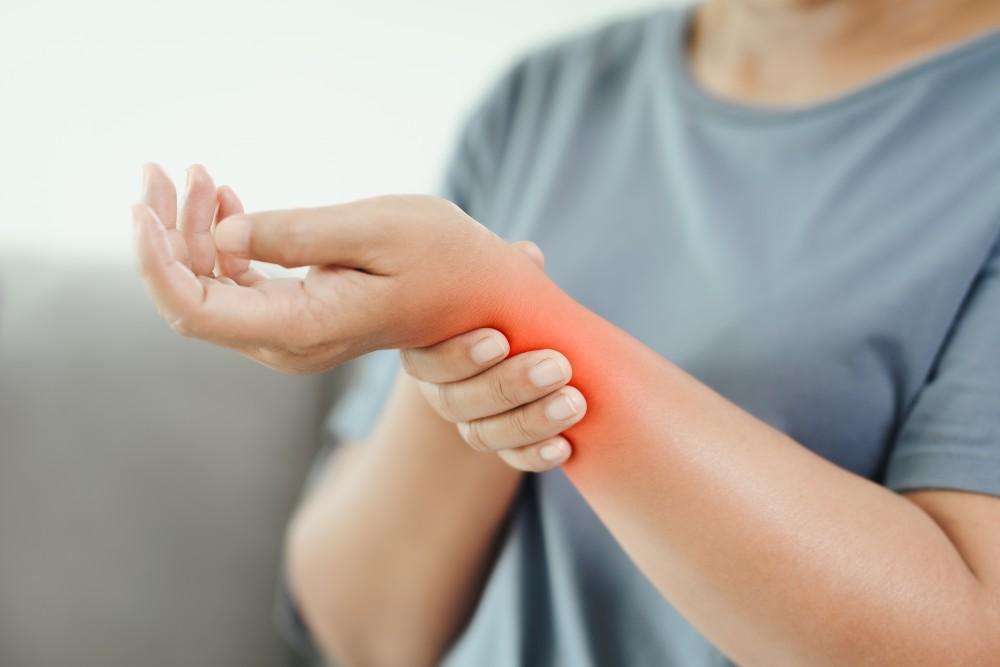
Wrist pain is a common complaint that can significantly impact daily activities, work, and overall quality of life. Whether caused by repetitive strain, injury, or underlying medical conditions, understanding the causes and effective treatment options is essential for relief and recovery. This article explores the various causes of wrist pain, effective home remedies, professional treatments, preventive measures, and lifestyle changes to promote healing.
Understanding the Causes of Wrist Pain
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to understand the common causes of wrist pain. Some of the most prevalent reasons include:
1. Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI)
Repetitive movements, especially in jobs or hobbies that require constant wrist motions, can lead to RSI. Activities such as typing, playing musical instruments, or sports can strain the wrist.
2. Tendonitis
Tendonitis occurs when the tendons around the wrist become inflamed due to overuse. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a specific type of tendonitis affecting the thumb and wrist.
3. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This condition is caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to symptoms like tingling, numbness, and pain, especially in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
4. Wrist Sprains and Strains
Injuries from falls, twisting motions, or awkward positions can cause sprains (ligament injuries) or strains (muscle or tendon injuries) in the wrist.
5. Arthritis
Various forms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can affect the wrist joint, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
6. Ganglion Cysts
These benign lumps can develop along the tendons or joints of the wrist, often leading to discomfort or pain.
Symptoms of Wrist Pain
Recognizing the symptoms of wrist pain can help determine the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Dull ache or sharp pain in the wrist
- Swelling or inflammation
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
- Tingling or numbness in the fingers
- Weak grip strength
- Pain that worsens with activity or certain movements
How to Fix Wrist Pain: Effective Remedies and Treatments
Here are some effective strategies to help relieve wrist pain and promote healing:
1. Rest and Modify Activities
Rest is crucial for recovery. If you notice pain during specific activities, take breaks and modify your movements to avoid aggravating the wrist. Use your other hand when possible to reduce strain on the injured wrist.
2. Apply Ice
Applying ice can help reduce swelling and numb the pain in the wrist.
- How to Do It: Wrap ice in a cloth or use an ice pack. Apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
- Tip: Avoid applying ice directly to the skin to prevent frostbite.
3. Use Compression and Elevation
Wearing a compression bandage or wrist brace can provide support and reduce swelling. Elevating the wrist above heart level helps minimize swelling.
- How to Do It: Use a supportive wrist brace during daily activities or at night. Keep the wrist elevated with pillows when resting.
4. Take Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- How to Do It: Follow the dosage instructions on the label. Consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about medication.
5. Perform Gentle Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Once the initial pain subsides, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can help restore flexibility and strength to the wrist.
Stretching Exercises
- Wrist Flexor Stretch: Extend one arm in front of you with your palm facing up. Use your other hand to gently pull back on your fingers until you feel a stretch. Hold for 15-30 seconds.
- Wrist Extensor Stretch: Extend your arm with your palm facing down. Use your other hand to press down on your fingers, stretching the top of the wrist. Hold for 15-30 seconds.
Strengthening Exercises
- Wrist Curls: Use a light dumbbell or a can. Rest your forearm on a table with your wrist hanging off the edge, palm facing up. Curl the weight upward, then lower it back down. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
- Reverse Wrist Curls: Similar to wrist curls, but with your palm facing down. This targets the wrist extensors.
6. Consider Ergonomic Adjustments
If wrist pain is related to your work environment, ergonomic adjustments can make a significant difference.
- How to Do It: Use a keyboard and mouse that promote a neutral wrist position. Adjust your workstation so that your elbows are at a 90-degree angle.
- Tip: Consider using wrist rests for your keyboard and mouse to reduce strain during prolonged use.
7. Explore Physical Therapy
If wrist pain persists, a physical therapist can develop a personalized rehabilitation program to address your specific needs. They may incorporate:
- Manual therapy: Hands-on techniques to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Strengthening and flexibility exercises: Tailored exercises to restore function and strength.
- Education on posture and ergonomics: Tips to help you avoid future injuries.
8. Consider Alternative Therapies
Some alternative therapies may provide additional relief for wrist pain:
- Acupuncture: Involves inserting thin needles into specific points to alleviate pain and improve healing.
- Massage therapy: Can help reduce muscle tension and improve circulation in the wrist and forearm.
- Chiropractic care: A chiropractor may use manual adjustments to address any misalignments contributing to wrist pain.
9. When to See a Doctor
If wrist pain persists despite home treatment, it may be time to seek medical attention. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest and home remedies
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers
- Swelling that doesn’t go down
- Decreased range of motion
- Pain that affects your ability to perform daily activities
Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to diagnose the underlying cause of wrist pain and recommend appropriate treatments.
10. Surgical Options
In some cases, surgery may be necessary, particularly for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or severe tendon injuries that do not respond to conservative treatments. Surgical options may include:
- Carpal tunnel release: To alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
- Tendon repair: To fix torn or damaged tendons.
- Joint surgery: To address significant arthritis or joint issues.
Preventing Wrist Pain
Taking proactive steps can help prevent wrist pain from recurring:
- Limit Repetitive Motions: Take regular breaks during activities that require repetitive wrist motions.
- Strengthen the Wrist: Engage in regular strengthening exercises to improve wrist stability and resilience.
- Use Proper Technique: Whether typing, playing sports, or lifting, use proper techniques to minimize strain on the wrist.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps maintain overall joint health and flexibility.
Conclusion
Wrist pain can be debilitating, but with the right strategies, it can be effectively managed and resolved. From home remedies and ergonomic adjustments to professional treatments, a comprehensive approach can help restore function and alleviate discomfort. If wrist pain persists, seeking medical advice is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes and implementing preventative measures, you can protect your wrists and enjoy a pain-free lifestyle.