Understanding Pediatric Rehabilitation
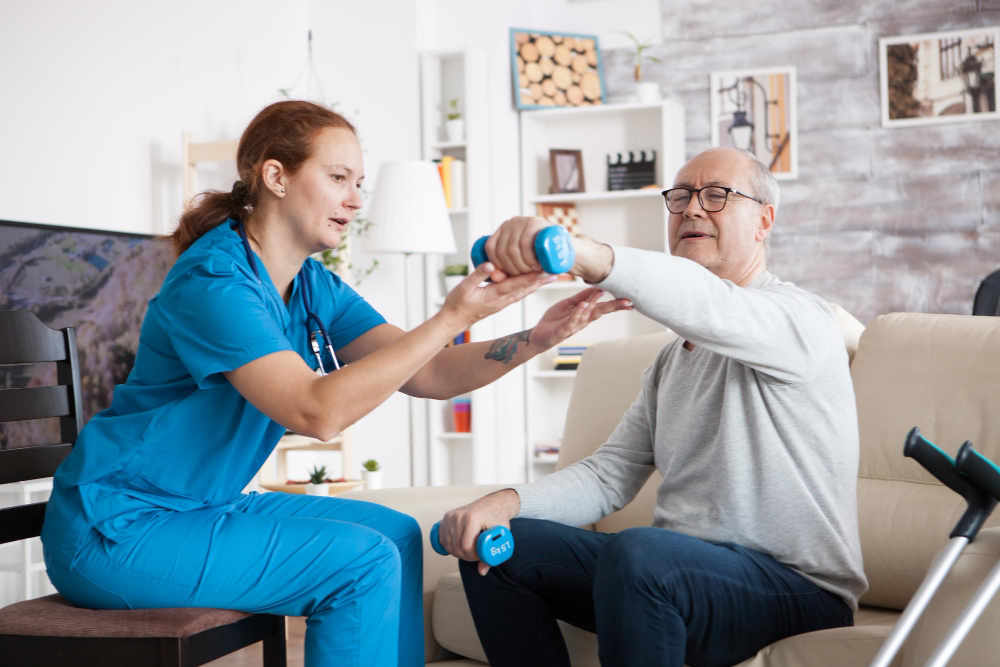
Strengthening exercises target specific muscle groups to improve strength and stability, reducing the risk of injury and enhancing athletic performance. These exercises involve progressively overloading the muscles to stimulate growth and adaptation, guided by a physiotherapist to ensure proper technique and safety.
The Importance of Early Intervention:
Early intervention is key in pediatric rehabilitation. The developing brain of a child possesses remarkable plasticity, making it highly responsive to therapeutic interventions. By identifying and addressing developmental delays or disabilities early on, we can significantly enhance a child’s long-term outcomes.
Conditions Treated in Pediatric Rehabilitation
Pediatric rehabilitation caters to a wide range of conditions, including but not limited to:
1. Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired movement and posture. It results from abnormal brain development or damage to the developing brain, often occurring before or during birth. CP manifests differently in each child, ranging from mild motor impairment to severe physical disability. Common symptoms include muscle stiffness, involuntary movements, and difficulty with coordination. Treatment for CP focuses on maximizing functional abilities and improving quality of life through a combination of therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech-language therapy. With early intervention and ongoing support, children with CP can achieve significant milestones and lead fulfilling lives.
2. Spina Bifida
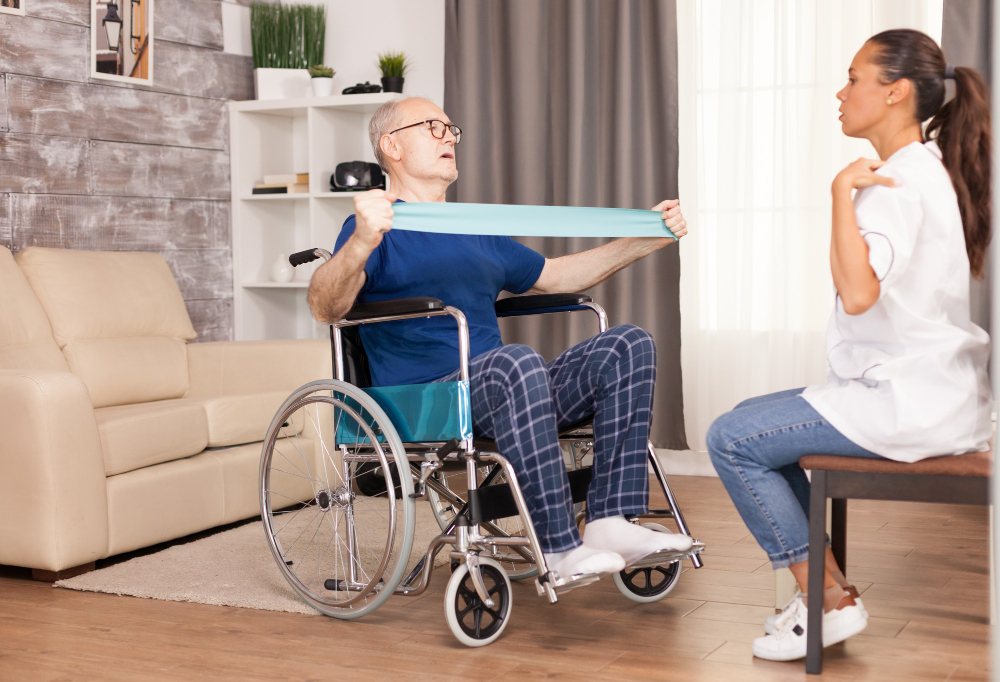
Spina Bifida is a complex neural tube defect that occurs during fetal development when the spinal column fails to close properly. This condition can lead to varying degrees of paralysis, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and orthopedic complications. Children with Spina Bifida often require lifelong medical care and rehabilitation to address mobility limitations and associated health issues. Treatment may include surgical interventions to repair the spinal defect, physical therapy to improve muscle strength and coordination, and assistive devices such as braces or wheelchairs to enhance mobility. Despite its challenges, with comprehensive care and support, children with Spina Bifida can lead fulfilling and independent lives.
3. Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. It affects various muscles throughout the body, leading to difficulties in mobility, balance, and coordination. Children with Muscular Dystrophy often experience challenges in performing daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and lifting objects. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing Muscular Dystrophy, focusing on strengthening exercises, stretching, and mobility aids to optimize function and delay disease progression. Additionally, occupational therapy can help children adapt to changes in their abilities and maintain independence in activities of daily living.
4.Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) are devastating events that can occur due to accidents, falls, or physical abuse, often resulting in long-term neurological impairments. Children who experience TBIs may face difficulties with cognition, communication, motor skills, and emotional regulation. Pediatric rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process, offering tailored interventions to address the unique needs of each child. Physical therapy focuses on restoring mobility and coordination, while speech-language therapy helps improve communication abilities. Occupational therapy aids in relearning daily activities and fostering independence. Through comprehensive care and support, pediatric rehabilitation strives to maximize the recovery potential of children with TBIs.
5.Developmental Delays
Developmental delays encompass a broad spectrum of challenges in children’s growth and milestones, affecting areas such as motor skills, speech and language, cognitive abilities, and social-emotional development. These delays can arise from various factors, including genetic conditions, premature birth, environmental influences, or neurological disorders. Addressing developmental delays requires a comprehensive approach, involving early screening, diagnosis, and intervention. Through targeted therapies and supportive interventions, children with developmental delays can make significant strides in their development, improving their overall quality of life and enhancing their opportunities for success in school and beyond.
6. Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders encompass a diverse range of conditions, each presenting unique challenges for children and their families. From chromosomal abnormalities to inherited metabolic disorders, these conditions can impact various aspects of a child’s development and well-being. In pediatric rehabilitation, addressing genetic disorders requires a comprehensive approach, combining medical management, therapy, and supportive care. Specialists collaborate closely to tailor interventions that mitigate symptoms, optimize function, and enhance quality of life. By understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms and utilizing cutting-edge therapies, pediatric rehabilitation strives to empower children with genetic disorders to thrive and overcome the obstacles they face.
Therapeutic Interventions
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on improving mobility, strength, and coordination. Through exercises, stretches, and assistive devices, physical therapists help children achieve their maximum functional potential.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy assists children in developing the skills needed for daily activities, such as dressing, feeding, and writing. Occupational therapists utilize play-based interventions to enhance fine motor skills and sensory processing.
Speech-Language Therapy
Speech-language therapy targets communication disorders, including speech articulation, language comprehension, and social communication. Therapists employ various techniques to improve communication abilities and enhance social interactions.
Overcoming Challenges in Pediatric Rehabilitation.
While pediatric rehabilitation offers tremendous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Limited access to services, financial constraints, and the emotional toll on families are significant hurdles that must be addressed.
1.Addressing Accessibility:
Addressing accessibility in pediatric rehabilitation involves implementing strategies to ensure that all children, regardless of location or socioeconomic status, can access the care they need. This includes establishing satellite clinics in underserved areas, offering telehealth services for remote consultations, and providing transportation assistance for families who face mobility challenges. Additionally, healthcare organizations can collaborate with community partners and advocacy groups to raise awareness about available services and advocate for policy changes that improve access to care. By addressing barriers such as geographical distance, financial constraints, and cultural considerations, we can create a more inclusive healthcare system that serves every child in need.
2. Providing Emotional Support:
Providing emotional support in pediatric rehabilitation involves addressing the multifaceted needs of both children and their families. It entails creating a nurturing environment where families feel heard, understood, and empowered. This support extends beyond the clinical setting, encompassing counseling services, support groups, and educational resources tailored to the unique challenges they face. It involves fostering resilience, coping strategies, and a sense of community among families, helping them navigate the emotional complexities of their journey. By recognizing the emotional toll of pediatric rehabilitation and offering comprehensive support, healthcare professionals can empower families to face challenges with strength, courage, and hope.
Empowering Dreams, Transforming Lives
Providing emotional support in pediatric rehabilitation involves addressing the multifaceted needs of both children and their families. It entails creating a nurturing environment where families feel heard, understood, and empowered. This support extends beyond the clinical setting, encompassing counseling services, support groups, and educational resources tailored to the unique challenges they face. It involves fostering resilience, coping strategies, and a sense of community among families, helping them navigate the emotional complexities of their journey. By recognizing the emotional toll of pediatric rehabilitation and offering comprehensive support, healthcare professionals can empower families to face challenges with strength, courage, and hope.